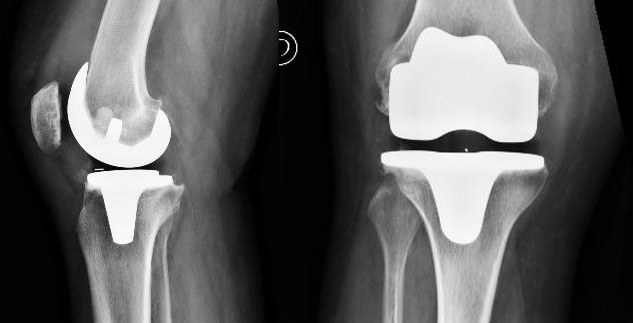
Total knee replacement (arthroplasty)
The knee joint consists of three parts: the femoral condyles, tibial plateau and patella. When we have a healthy knee, the cartilage that covers the components is smooth, soft and allows movement without pain. As a result of a damaged cartilage, the patient begins to feel pain, stiffness and function limitation, reducing the quality of life.
Different diseases cause joint damage, the most common being osteoarthritis, rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, etc…
A total knee replacement involves replacing the knee joint, which has suffered significant wear, with a prosthesis.
Benefits of intervention
This prosthesis will allow to regain normal knee function, eliminating the pain suffered by these patients both when walking and at rest. In this way the patient will be able to recover the lost quality of life and walk normally again.
Total knee arthroplasty is one of the most successful surgeries in the history of medicine, because 95% of patients achieve good to excellent results, and implant survival rates ranged from 94% between 10 to 15 years.
The success of surgery depends on the exercises performed by the patient, taking into account the precautions recommended for your knee, not to mention having a healthy lifestyle.
Medical-technical description
There are different models of prosthetic knees,available today. Each prosthesis is suited for the patient's specific needs, and that is why the treatment is individualized for each one, with the implant of prosthesis that best meets their needs. To sum up, the different types of prostheses available today are:
- Total Knee Arthroplasty: after resecting the diseased areas of the femur, the tibia and patella arthrosis, two or three components must be implanted: one in the tibia with a central stem that is inserted into the tibia; another in the femur that approximately follows the shape of the distal femur and has a pivot for better grip of the bone. And if necessary another one, spherical shaped, to articulate with the femur and a flat surface to anchor the bone pivots. The prosthesis is attached to the bone with bone cement. This is the most common technique nowadays in active patients, offering the patient greater mobility with adequate stability of the knee. The materials that make up the prosthesis ensure long life of the implants
- Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: in these cases, only an area of the knee is changed. They are of different types:
- Unicondylar knee prostheses: if the disease affects only one compartment either internal or external. This prosthetic surgery allows preservation of bone and a faster recovery. It is considered the most economical in cost.
- Patellar prosthesis: when the disease primarily affects the patellofemoral joint, replacement can be unique to this area of the problem - Prosthetics Review: when switching a primary prosthesis or when there is a deformity
There exist cemented and uncemented components listed according to the morphology of the knee to be treated and the quality of its bone mineral density, age of patient, etc…
The Procedure
The total knee replacement is performed in the operating theatre. The surgery takes usually one hour, while the patient remains in the operating room and in a recovery area for 3 to 5 hours. The patient will be hospitalized from 3 to 4 days.
Preoperative measures
Prior assessment at the clinic, deciding and stating the specific aspects of the surgery and giving informed consent.
- You must provide a comprehensive list of medicines you take regularly (including herbal medicines) at the time of the operation
- Conducting a preoperative evaluation consisting of a blood test, biochemistry, coagulation, chest radiograph and ECG
- Wash previous night and morning with antiseptic soap, the area to undergo surgery. If desired, you can shave the knee at home the day before the intervention, from mid-thigh to mid leg
- You must cut your toenails, because you will be unable to do so until 12 weeks after surgery
- You should plan your convalescence at home after surgery. Seek family, neighbors, social assistance for your shopping, personal hygiene, to get food, etc…
- Get a high stool or chair for kitchen and bathroom, as well as a supplement for the toilet bowl. The seat must be high so that your knees are not higher than your hips
- If surgery is scheduled in the morning, you must go to hospital on an empty stomach. If it is in the afternoon, have an early breakfast and do not take food or drink from 9 am
- Do not wear any metal object during operation (rings, bracelets, earrings, piercing, etc.)
Postoperative care
- You will be provided with a compressive elastic bandage, which can be kept while in bed. Drains will be removed the day after surgery. In the following days an elastic compression stocking will be applied to the thigh, which must be kept for at least 3 months
- The movement starts from the first day. The load may be limited to 50% during the first 6 weeks until the start of osseointegration in uncemented arthroplasties, or will be complete in cemented ones.
- You must receive thrombo and antibiotic prophylaxis
- You may need to use a walker at first, and an English cane afterwards
- After 6 weeks you may do strengthening exercises for restrenghthening the abductor muscles. They usually achieve a full range of motion in the 6 or 8 weeks following the surgery regularly
- Once discharged, you should contact us if you have chest pain or shortness of breath, pain, swelling or redness in one leg, sudden pain in the operated knee, or fever and chills processes
- Once discharged, likewise, you must avoid the following movements and postures for 3 months to avoid damage and possible dislocation of your new knee
- Do not put your knees higher than your hips when sitting
- Do not bend over to pick things from the floor
- Avoid twisting your operated leg in or out while sitting or lying down
- Avoid heavy lifting
You can also download the Inform Consent from the Official Website of SECOT, la Sociedad Española de Cirugía Ortopédica y Traumatología